The Current State of DeFi – The Search For Real Yield
As the DeFi economy grapples with a bear market and the threat of looming regulation, one question is driving investors as they evaluate old and new protocols alike:
Where is the underlying value?
Or put an old-fashioned way, what does this protocol offer its users?
One answer to that question is the idea of “real yield”, a topic that has generated increasing buzz in the crypto world. To understand what real yield is – and how Minterest provides real yield – you need to start with the current state of DeFi: where it is, what went wrong, and how DeFi 2.0 promises to improve.
- DeFi’s Untapped Potential
- DeFi: New Financial Model, Same Old Problems
- Maturing Markets
- Finding Real Yield
DeFi’s Untapped Potential
DeFi (Decentralized Finance) refers to a growing ecosystem of financial applications built on blockchain technology that aim to provide financial services without the need for traditional intermediaries such as banks or financial institutions. The last crypto bull run saw easy money pumped into DeFi in vast quantities, fueled by the sector’s vast potential:
- Decentralized exchanges, for peer-to-peer trading of cryptocurrencies and other assets without the need for a centralized exchange.
- Lending and borrowing platforms, enabling users to earn interest on their assets or to borrow funds from others using smart contracts to manage the terms and conditions of the loans.
- Stablecoins, tying digital assets to a stable asset such as the US dollar, allowing for more stability in volatile crypto markets.
- Tokenization, converting traditional assets such as real estate or art into tokenized form and making it possible to trade those assets.
But in the rush to claim the vast wealth DeFi promised, new protocols started to take shortcuts. DeFi startups lured retail investors, flush with cash, by promising sky-high yields. Unsustainable yield farms grew in popularity, fueled by ever-greater demand.
What drew users in? Part of the allure was found in DeFi’s inherent advantages over TradFi. With DeFi, anyone could access advanced financial tools; borrowing and lending functions were no longer walled off behind staid financial institutions and vested interests.
DeFi held immense promise as an entirely new financial model. Unfortunately, in the rush to build a new model, DeFi began to repeat some of TradFi’s mistakes.
DeFi: New Financial Model, Same Old Problems
The early wave of DeFi protocols – DeFi 1.0 – eventually developed a set of core problems that were exposed dramatically during the crypto crash of 2022.
Complexity
Many DeFi platforms were difficult for average users to understand, leading to potential security risks and difficulties in accessing the platform.
Centralization
Despite being marketed as decentralized, many DeFi platforms were highly centralized and controlled by a small group of individuals, undermining the decentralized nature of DeFi and leaving it open to manipulation.
Market Volatility
DeFi proved highly susceptible to market volatility with dramatic and rapid price changes. As ETH went, so did the market; at its peak, the Ethereum blockchain was responsible for nearly 97% of DeFi TVL. That market share has since decreased to around 60% as more players have entered the DeFi space, providing some much-needed flexibility.
Fraud
Ponzi schemes abounded in DeFi 1.0, as bad actors took advantage of the hype and capitalized on DeFi’s unknowns. This was the case for many protocols that only produced high yields by relying on a steady stream of fresh liquidity, primarily from retail investors.
Scalability/Sustainability
DeFi 1.0 largely rode the wave of the crypto bull market, foregoing long-term development in favor of short-term gains.
The bear market forced a reckoning. Fraudsters were exposed, poor business practices came to light, and major players in the sector (3AC, Celsius, FTX, etc.) collapsed.
Maturing Markets
In the aftermath, a new vision for DeFi emerged. Despite DeFi 1.0’s problems, it served as a clear proof-of-concept. The market wanted DeFi exchanges, borrowing and lending protocols, tokenization, etc. The underlying use cases were sound, even if numerous protocols didn’t hold up.
In fact, DeFi 1.0, and the resulting crash, bears strong similarities to an earlier tech market cycle: the dot-com bubble of the late 90s and early 2000s.
Note this comparison of the two:
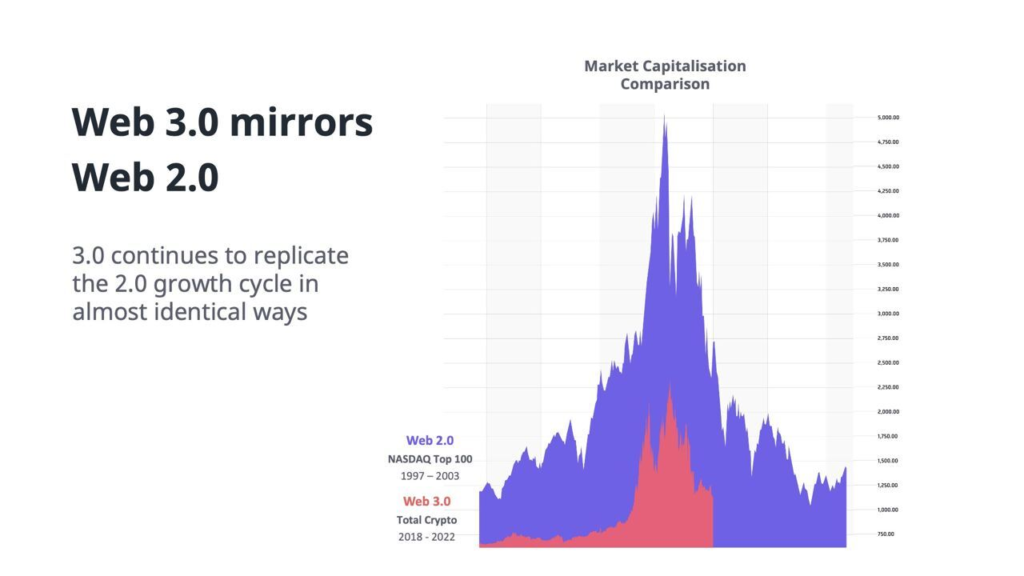
Dot-com companies crashed – hard – in the early 2000s. In fact, value just after the initial crash rested at a level not much higher than before the boom took off. On the surface, dot-coms seemed to be right back where they started a few years before.
Zoom out, and a vastly different story emerges.
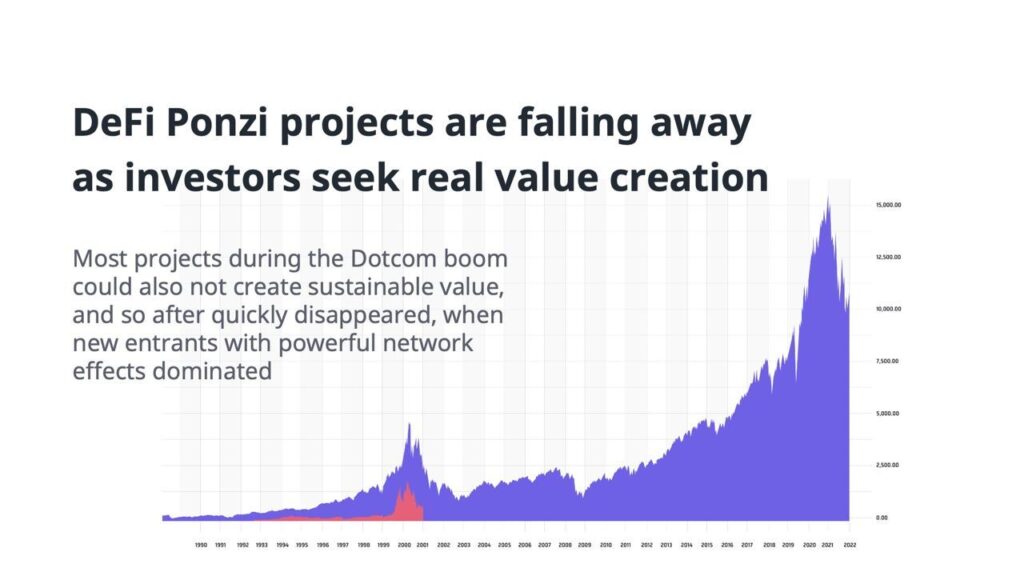
When the dot-com bubble burst, two things happened:
- Companies with poor underlying fundamentals failed.
- The underlying technology grew.
Why? Because there was genuine underlying value in the technology – just not in most of the applications.
DeFi 2.0 finds itself in the same position.
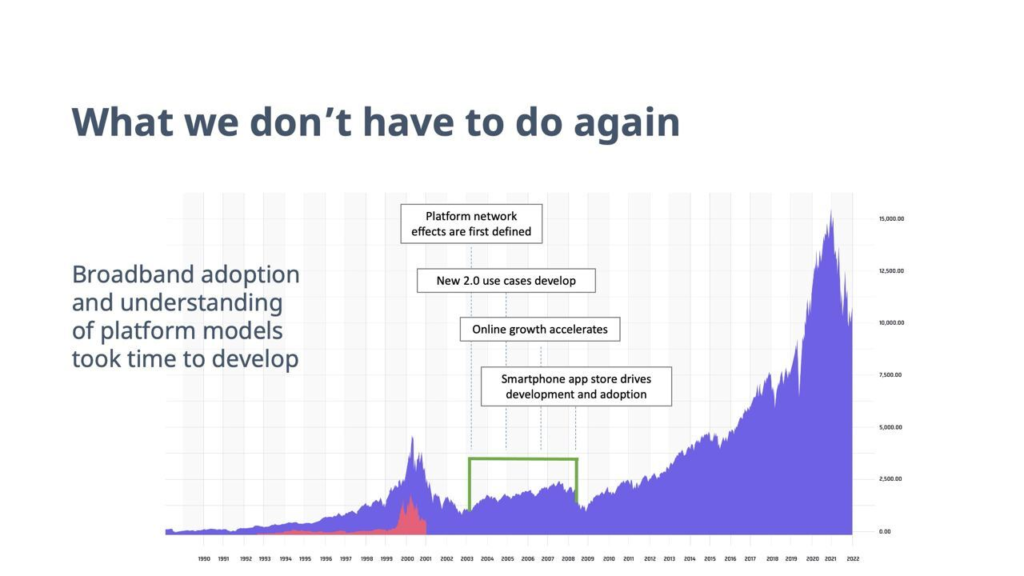
There’s a renewed emphasis on sustainability and profitability. With the hype largely gone from the market, investors can evaluate projects more clearly.
On the project side, new DeFi protocols need to deliver clear value based on rock-solid industry fundamentals. And in typical crypto fashion, this search for underlying value has led to a new term: real yield.
Finding Real Yield
Real yield implies sustainability and value. Gone are the sky-high yields of Anchor Protocol and a yield-farming model built on attracting an endless stream of new investors. DeFi 2.0 relies on real yield, returns based on protocols that meet proven use cases and have a clear path to profitability.
DeFi 2.0 also involves a return to the core principles that set DeFi apart from traditional finance, including:
- Decentralization
- Accessibility
- Trust
- Reduced costs
- Speed
Minterest leads the charge towards DeFi 2.0, building a protocol with solid fundamentals to create genuine underlying value. It’s that value that powers real yield in a way that DeFi 1.0 never did.
How does it work? Read the whitepaper here, or watch a breakdown of how Minterest outcompetes other protocols.
Next up: What Works (And What Doesn’t) In DeFi: How current DeFi protocols generate value.
06, February 2023